Spending Money Wisely: A Beginner’s Guide for Kids
Money is an important aspect of our lives, and it is never too early to start learning how to manage it. Whether it’s receiving an allowance, doing chores for extra cash, or receiving monetary gifts on special occasions, kids have various ways of getting money. Therefore, it is crucial to teach them how to spend money wisely from a young age to avoid bad financial habits later on.
As a parent, teaching your child about money management can be a daunting task, but it is an essential life skill that can benefit them in the long run. While it may seem daunting, introducing basic money management concepts at an early age can help set a foundation for responsible financial behavior in the future. In this guide, we will provide some tips and tricks for teaching your kids how to spend money wisely.
The Importance of Money Management Skills for Kids
Money management is a critical life skill that everyone needs to have, regardless of age. Teaching kids about money management early on can help them make informed financial decisions, avoid debt, and live a financially stable life. Developing good money habits early in life can lead to a lifetime of responsible financial behavior, which is essential in today’s society.
Understand the Value of Money
It is essential to teach children the value of money and how to appreciate it. One way to do this is by giving them an allowance and encouraging them to save some of it. Children need to learn that money is a finite resource, and they must learn how to budget and prioritize their spending. When children are given an allowance, they learn the value of earning money, and they learn to make informed decisions about how to spend it.
Teach Them to Budget
Learning to budget is one of the essential money management skills that kids need to develop. The earlier they learn to budget, the better equipped they will be to manage their money effectively. One way to teach kids how to budget is by helping them set a savings goal, such as saving for a toy or a game. Encourage them to save a portion of their allowance each week, and once they reach their savings goal, reward them. This will teach them the value of setting goals and working towards achieving them.
Encourage Smart Spending
Teaching kids how to spend money wisely is an essential part of money management. Encourage them to think carefully before making purchases and to consider whether the item they want is a need or a want. Help them understand that they cannot buy everything they want, and they need to prioritize their spending. Teach them to compare prices and look for sales, and encourage them to consider buying used or refurbished items when possible.
Lead by Example
Children learn by example, so it is essential to lead by example and model responsible financial behavior. Be open and honest with your kids about money matters, and involve them in family financial decisions. Talk to them about saving for the future and the importance of avoiding debt. Encourage them to ask questions and be curious about financial matters.
Make Learning Fun
Learning about money management doesn’t have to be boring. There are plenty of fun and creative ways to teach kids about money. For example, you can use board games or online games to teach them about budgeting and saving. You can also encourage them to start a business or a lemonade stand to earn some extra money. These activities can help kids learn valuable money management skills while having fun at the same time.
Teach the Basics of Banking
Learning about banking is an essential part of money management. Teach your kids about the basics of banking, such as opening a savings account, depositing money, and earning interest. Show them how to use an ATM and how to check their balance online. These skills will help them become more financially independent as they get older.
Encourage Generosity
Teaching kids about money management isn’t just about saving and spending; it’s also about giving back. Encourage your kids to be generous with their money and to donate to charity or to help those in need. This will teach them the value of giving and help them develop empathy and compassion towards others.
Incorporate Real-Life Scenarios
It’s essential to incorporate real-life scenarios into your child’s financial education. For example, when you go grocery shopping, involve your child in the process of creating a shopping list and setting a budget. Teach them how to compare prices and make informed decisions about what to buy. When you pay bills, explain to your child what the bills are for, and how you budget for them. These real-life scenarios can help your child understand the practical application of money management skills.
Teach the Consequences of Poor Money Management
It’s important to teach children the consequences of poor money management. For example, if they spend all their allowance in one day, they will have nothing left for the rest of the week. Teach them about the dangers of debt and how it can impact their financial future. Explain to them the consequences of making impulsive purchases and not budgeting for their expenses. These lessons can help your child understand the importance of responsible financial behavior.
Encourage Saving for the Future
Teaching kids to save for the future is an essential part of money management. Encourage your child to save a portion of their allowance each week and to set long-term savings goals. For example, they could save for a college fund, a car, or a down payment on a home. Encourage them to track their progress and reward them when they reach their savings goals. These habits will help your child develop a sense of financial responsibility and plan for a secure future.
Start Small
It’s important to start small when teaching kids about money management. Begin by teaching them basic concepts such as saving, budgeting, and spending wisely. As they get older, you can introduce more complex topics such as investing, credit, and debt management. By starting small and building a strong foundation, your child will be better equipped to manage their finances as they grow older.
Teaching kids about money management is an essential life skill that can benefit them in the long run. By introducing basic money management concepts at an early age, you can help your child develop responsible financial behavior that will last a lifetime. Encourage them to save, budget, spend wisely, and be generous with their money. Lead by example and incorporate real-life scenarios into their financial education. By doing so, you’ll help your child develop the skills and knowledge they need to be financially independent and secure in the future.
Spending money wisely is a crucial life skill that kids must learn at an early age. With the help of FINSTART, kids can learn to manage their finances, create a budget, prioritize their expenses, avoid impulsive buying, save for the future, and even earn money. Teaching these skills to kids will set them up for a successful financial future, and empower them to make informed financial decisions.
The ABC’s of Money for Kids
Just as we use the alphabet “A for Apple” “B for Ball” etc. to teach our kids the English language, let’s also teach them the language of money using the ABCs of money.
A – ASSET
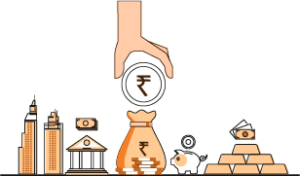
Assets are the things you own, and can be sold to get money.
B – BANK
A place that looks after people’s money, keeps it safe and lends money to people to help them buy things like houses.
C – CURRENCY

Consists of paper money and coins. It is the official money of a country. Each country has its own form of currency –
India – Rupee
USA – Dollar
United Kingdom – Pound
D – DEPOSIT
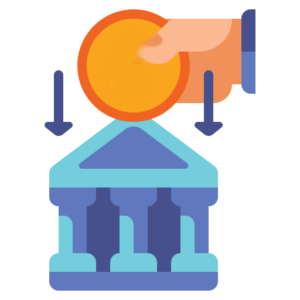
A deposit is when people put money IN the bank.
E – EARNINGS
The money people receive by doing any work is called earnings.
F – FINANCE

Management, creation and study of money.
G – GOODS

Things that people make or grow to sell. Like Toys, Laptops, Apple etc.
H – HEDGE

A plan to reduce risk.
I – INTEREST
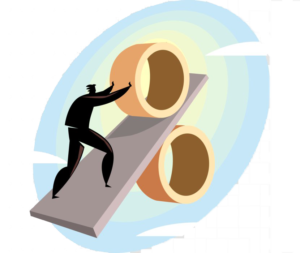
A reward for saving and cost of borrowing.
J – JOINT ACCOUNT
A bank account, where money is shared by two or more people.
K – KYC

KYC means Know Your Customer. A process of verifying the identity of the customer.
L – LOANS

Money that people borrow from someone for a specific reasons with a promise to pay back.
M – MONEY

Money is what people use to buy things. Medium of exchange.
N – NEEDS

Things people must have to live.
O – OPPORTUNITY COST
When people give up something to do something else.
P – PROFIT

Income – Expenses = Profit
The money made by a business.
Q – eQuity
Represents ownership in a company.
R – RISK

A chance of getting hurt or losing something.
S – SAVING

The money people sets aside and decides not to spend.
T – TAX
A sum of money that people pay to the government for the services provided by the government.
U – UNBANKED

When a person does not have or use a bank account.
V – VALUATION

The process of determining the worth of an asset.
W – WANTS

Things that are nice to have but not necessary to survive.
X – eXpense

The money spent to purchase things.
Y – YIELD

The extra money people make by investing their money.
Z – ZERO BALANCE ACCOUNT

A bank account in which people can have “0” money.
Teaching children the basic words of money from an early age will help them as they grow and enter the real world. Finstart is a platform where your child can learn the language of money in a fun and interactive way.
Contact us to know more about our programs.
The Power of Saving: How to Build a Strong Financial Foundation
Financial stability is one of the most crucial aspects of life that determines our well-being, peace of mind and our ability to achieve our goals and aspirations. Building a strong financial foundation is a gradual process that requires discipline, patience, and a strong commitment to saving. The power of saving is immense, and it is something that can help individuals to achieve financial security and independence, no matter what their current financial situation may be.
The Importance of Saving
Saving is the foundation of financial stability and security, as it provides individuals with a cushion against unexpected expenses, emergencies and allows them to plan for the future. By developing a savings habit, individuals can ensure that they have access to the funds they need to meet their financial obligations and pursue their goals. Additionally, saving helps to reduce stress and anxiety about money, and it provides individuals with the peace of mind that comes from knowing that they have a safety net in place.
Setting Financial Goals
The first step in building a strong financial foundation is to set financial goals. Goals provide direction and purpose and help individuals to focus their efforts and stay motivated. When setting financial goals, it is essential to consider both short-term and long-term objectives. Short-term goals might include paying off debt, building up an emergency fund or saving for a down payment on a house. Long-term goals might include saving for retirement, starting a business or paying for a child’s education.
Creating a Budget
Once you have set your financial goals, the next step is to create a budget. A budget is a plan for how you will allocate your income and expenses, and it is essential for ensuring that your spending aligns with your goals. A budget helps individuals to track their spending, identify areas where they can cut back, and prioritize their spending. There are various budgeting methods available, including the 50/30/20 rule, the envelope method, and the zero-based budget. Individuals should choose the method that works best for them and stick to it.
Saving Automatically
Automatic savings is one of the most effective ways to build a strong financial foundation. By setting up automatic transfers from your checking account to your savings account, you can ensure that you are saving regularly and consistently. This can help individuals to overcome the challenges of discipline and motivation and ensure that they are making progress towards their financial goals.
Reducing Debt
Reducing debt is another important aspect of building a strong financial foundation. High levels of debt can have a significant impact on an individual’s finances and can prevent them from saving and investing effectively. To reduce debt, individuals should prioritize their payments and focus on paying off high-interest debt first. Additionally, they should consider ways to increase their income, such as taking on a side job, negotiating a raise or selling assets they no longer need.
Investing for the Future
In addition to saving, investing is another crucial component of building a strong financial foundation. Investing allows individuals to grow their wealth over time and achieve their long-term financial goals. There are various investment options available, including stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and real estate. When investing, it is important to consider factors such as risk tolerance, investment goals and the length of time you plan to invest for.
Building an Emergency Fund
An emergency fund is an essential component of a strong financial foundation. An emergency fund provides individuals with a cushion against unexpected expenses and emergencies, such as job loss, medical bills, or home repairs. The goal of an emergency fund is to have three to six months’ worth of living expenses saved. By having an emergency fund in place, individuals can reduce the stress and anxiety associated with unexpected expenses and ensure that they have the funds they need to weather a financial crisis.
Managing Credit
Credit is an important tool that can help individuals to build wealth, but it can also be a source of financial stress if not managed properly. To build a strong financial foundation, it is important to maintain a good credit score and manage credit responsibly. This means paying bills on time, avoiding high levels of debt, and monitoring your credit report regularly to ensure that all information is accurate.
Protecting Your Finances
Protecting your finances is an important part of building a strong financial foundation. This includes protecting against identity theft, fraud, and other financial crimes. It is essential to safeguard personal information, such as social security numbers, bank account information, and passwords. Individuals should also invest in insurance, such as life insurance, health insurance, and property insurance, to protect against financial loss.
Incorporating Healthy Financial Habits
Incorporating healthy financial habits is an important part of building a strong financial foundation. This includes regularly reviewing and updating your budget, avoiding impulse purchases, and seeking professional financial advice when needed. Staying informed about personal finance and seeking educational resources, such as books, podcasts, and online courses, can also help individuals to make better financial decisions. Additionally, being mindful of how money is spent and making informed choices about expenses can help individuals to stay on track and achieve their financial goals.
The Power of Compound Interest
The power of compound interest should not be underestimated when it comes to building a strong financial foundation. Compound interest is the interest earned on an investment, plus the interest earned on the interest. Over time, compound interest can result in substantial growth, making it an effective tool for building wealth. For example, by investing just Rs.500 per month into a SIP, an individual could potentially have several lakhs saved by the time they retire.
Stay Committed
Building a strong financial foundation requires a long-term commitment and a dedication to saving and investing regularly. It is important to stay committed to financial goals and to remain disciplined, even when faced with obstacles or temptations to spend. Remember, building wealth takes time and patience, but the power of saving and investing can help individuals to achieve financial security and independence.
Building a strong financial foundation is a process that starts at an early age and lasts a lifetime. Finstart is dedicated to helping young individuals establish a strong financial foundation by teaching them the basics of finance in an interactive and engaging way. By learning the importance of saving, budgeting and investing from an early age, young individuals can develop good financial habits that will benefit them throughout their lives. Practicing these habits from an early age can help establish a strong financial foundation and set individuals on a path towards financial security and independence. Finstart provides a comprehensive curriculum and interactive tools to help young individuals understand the value of their money and make informed financial decisions.
Start your child’s financial journey with Finstart today. Contact us for more information and to join our mission of promoting financial literacy.!!
Should We Start Teaching Our Children About MONEY?
There are a lot of things we wish, we had learnt back when were young; like how to delegate our homework in school or how not to get caught cheating in an exam. Wouldn’t school life be much easier with these skills and not to mention, these skills would come in handy in as an adult too, maybe.
Silly stuff and shortcuts aside, there are in fact few things in life, which we do regret not learning in early stages of life; like the importance of finance and wealth. The whole concept of building, growing and managing personal finance, is so wrongly portrayed and conveyed in our generation, that our kids as well have not quite understood the crux of money.
Finance doesn’t just mean savings and investment. It begins with the understanding of money from its roots; how is it made, how much is spent vs how much do we need to spend, how to prioritize expenses and how to earn stability of income and to grow it.
Let’s take an example of a 10 year old kid who is allowed a pocket money of Rs.100 only in a month, to spend on anything he likes. On the 7th day of the month, the kid has bought himself a 50 rupees toy and a 50 rupees coloring book. The kid is happy because all he ever wanted in the first week of allowance fits his pocket money exactly. However, there are still 3 weeks left and the kid might still need new pens at the end of week 3. There is no one who has taught him the significance of prioritization, the basic difference between a need and a want and even is unaware of the concepts of savings and provisions.
Forget school life, even our teen life in college would have been much better, if we were taught these basic things about money. Our career decisions could have shaped better, if we had some fundamentals of how money works.
Recent studies say that children cultivate habits at as early age as 7 years old. They subconsciously imprint things they saw their parents doing and repeat the same, while growing up. If we are imparting morals and knowledge when kids barely know the difference between right and wrong, why are we not imparting the knowledge of wealth. Sure the kid doesn’t have to know how share market works, but why can’t they learn where money comes from and how is it utilized.
Schools being the primary mode of teaching anything to a student would be the best place to kick-start this. If schools were to include financial literacy in their extra-curricular along with other activities like sports, music, dancing etc,, our next generation is sure to become wiser and smarter than us, who not only can do their own taxes but can also make good decisions in investments of personal finance
I know what are we all thinking, isn’t a 7 year old kid anyway leading a very hectic school life, with numerous subjects, several extra-curricular activities? However, what we fail to see is that this is not merely an activity or a subject to learn to pass an exam, but is a necessary life skill which each one of us needs in life, because surviving isn’t just enough, we need our upcoming generations to thrive. They need to learn the perspective of best out of waste and a difference between being a miser and being just resourceful.
There are lots of different innovative and creative ways schools can acquaint the children about these basic concepts of finance. With the right set of faculties or partners, a subject like financial literacy can also become as interesting as learning dancing or painting, We hope going forward; we will see schools actively engaging their kids in the concepts of financial literacy.
In the mean time, if you have any questions or want to understand more about the importance of Financial Literacy for the kids aged between 7-14 years, reach out to us at: https://finstart.in/contact-us/